
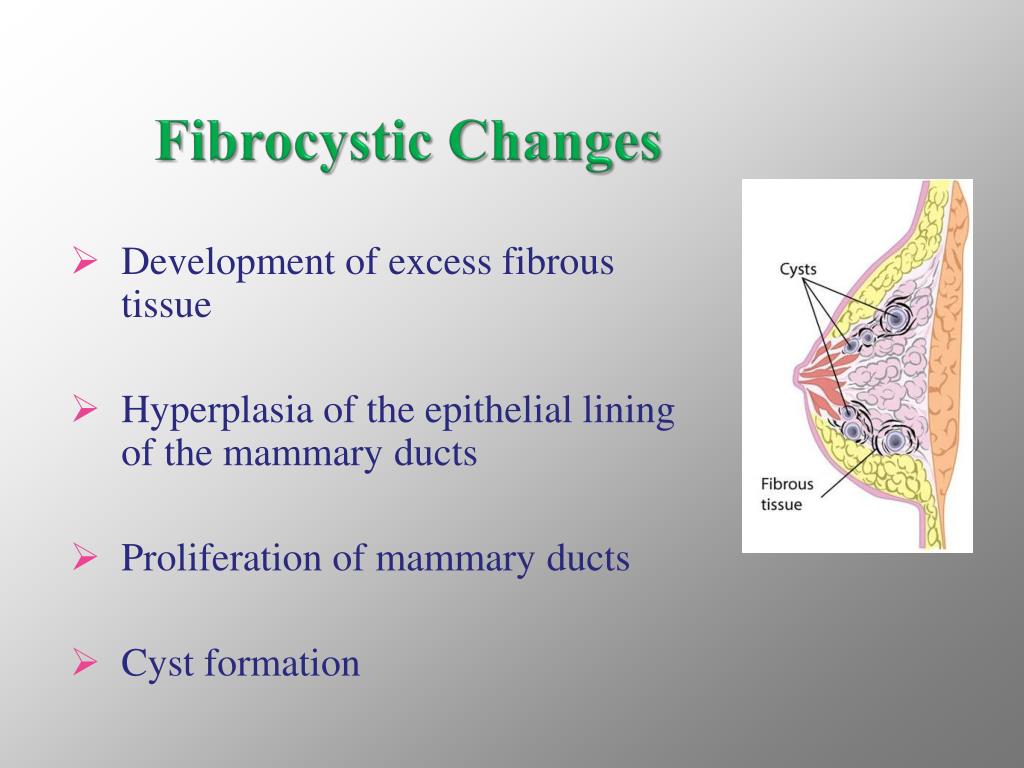

These changes do not appear to significantly increase the risk for breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Management includes observation, supportive measures, and altering hormone therapy, as needed. Ewing Sarcoma (if needed) to exclude malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax. The work-up involves imaging, with mammogram or ultrasound, and biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Breasts: Anatomy, and/or cyclic breast pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Clinician–Patient Relationship typically present with a breast mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast, “lumpy” or firm breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Menopause can only be diagnosed retrospectively, after 12 months without menstrual bleeding. Gonadal Hormones, and often diminish or resolve with menopause Menopause Menopause is a physiologic process in women characterized by the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity. Progesterone, converted from pregnenolone, also serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of gonadal steroid hormones and adrenal corticosteroids. It is required in embryo implantation pregnancy maintenance, and the development of mammary tissue for milk production. Progesterone acts on the uterus, the mammary glands and the brain. Ovaries: Anatomy and progesterone Progesterone The major progestational steroid that is secreted primarily by the corpus luteum and the placenta. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female sex characteristics. Changes are stimulated by both estrogen Estrogen Compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of estradiol. Examination of the Breast are seen in up to 50–60% of women, most commonly between 30–50 years of age. The fibrocystic breast has a dense irregular, lumpy, bumpy consistency. There are three major patterns of morphological changes, including fibrosis, formation of cysts, and proliferation of glandular tissue (adenosis). Fibrocystic changes Fibrocystic changes A common and benign breast disease characterized by varying degree of fibrocystic changes in the breast tissue.
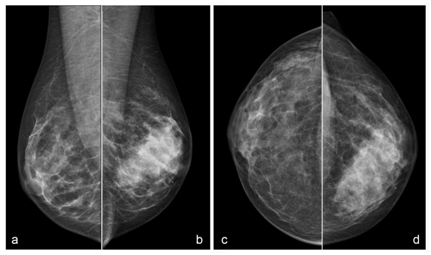
These are non-proliferative lesions, which include cystic and fibrous tissue formation. The classifications are based on subsequent cancer risk in either breast.
FIBROCYSTIC BREAST CHANGES PRO
Students: Educators’ Pro Tips for Tough Topicsįibrocystic change of the breast is a non-specific term referring to several types of benign breast conditions Benign breast conditions Benign breast epithelial lesions are grouped histologically as nonproliferative, proliferative without atypia, and atypical hyperplasia.Maternity Nursing and Care of the Childbearing Family.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
